Create High-Resolution Surface Models in Minutes, No GIS Expertise Required
What Is a Digital Surface Model?
A DSM is a three-dimensional representation of the Earth’s surface that includes everything visible from above. Unlike bare-earth models, a DSM captures the “first return” elevations, the highest points detected when scanning from above.
Think of a DSM as a snapshot of what you would see if you draped a sheet over a landscape. Every rooftop, treetop, and ground surface appears at its true elevation above a reference datum.
DSMs are stored as raster grids where each cell contains an elevation value. Common resolutions range from 30 meters for satellite products down to centimeter-level detail from drone surveys.
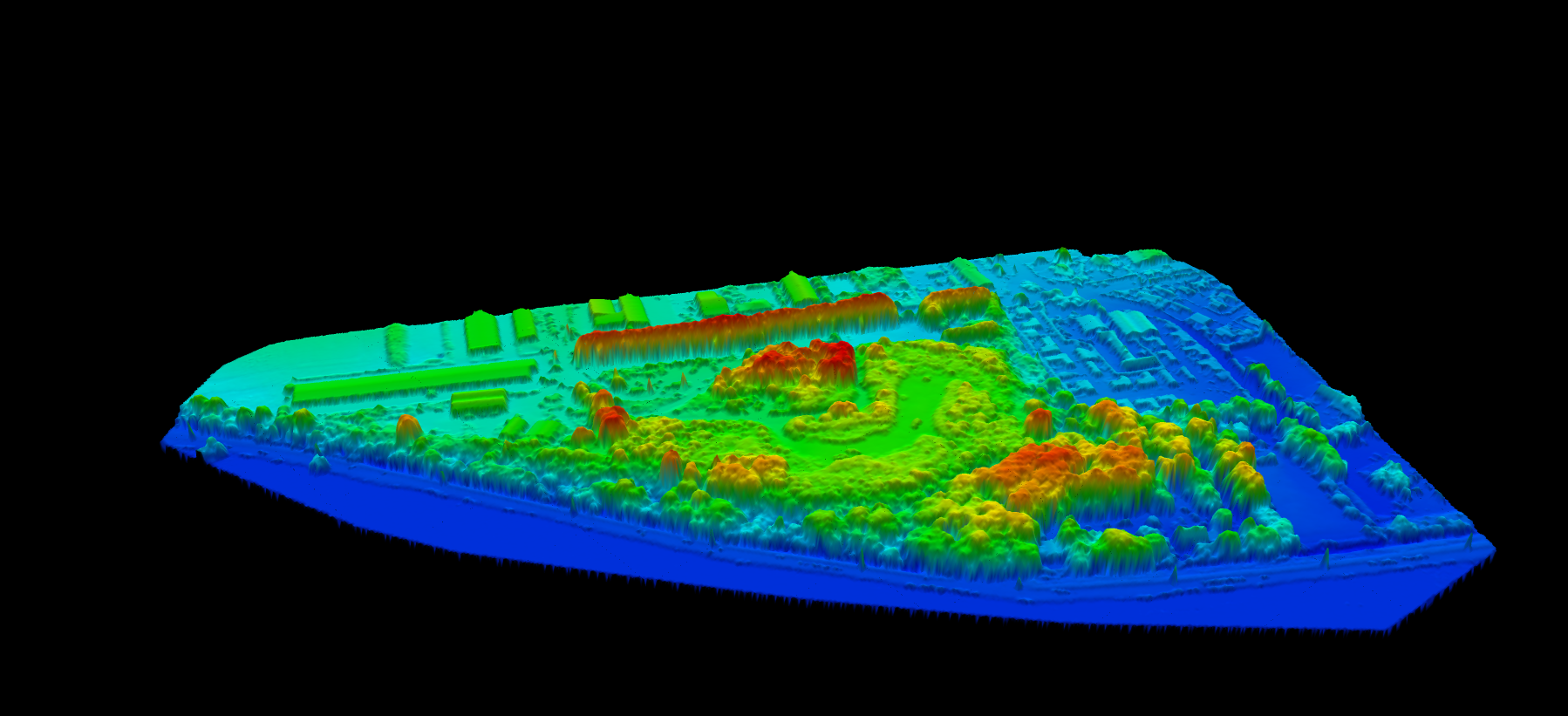
DSM vs DTM vs DEM
The terms DEM, DTM, and DSM are often confused, but they represent distinct products with different applications.
| Feature | DSM | DTM | DEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Includes buildings | Yes | No | Varies |
| Includes vegetation | Yes | No | Varies |
| Shows bare earth | No | Yes | Varies |
| Used for hydrology | Rarely | Yes | Yes |
| Used for urban planning | Yes | Rarely | Varies |
The Normalized DSM (nDSM)
A normalized DSM represents object heights above the ground rather than absolute elevations. It is calculated by subtracting the DTM from the DSM:
nDSM = DSM − DTM
The nDSM is particularly valuable for measuring building heights, calculating tree canopy heights (CHM), estimating vegetation biomass, and identifying above-ground obstructions for flight planning.
How Digital Surface Models Are Created
Several technologies can generate DSMs, each with distinct advantages. LiDAR is the most accurate method.
01
Data Acquisition
Drone or aircraft collects point cloud data with millions of laser pulses per second.
02
Classification
Points labeled as ground, vegetation, building, and other classes automatically.
03
Surface Generation
Interpolation creates a continuous raster surface from first-return points.
04
Export
DSM saved as GeoTIFF ready for GIS analysis, urban modeling, or forestry tools.
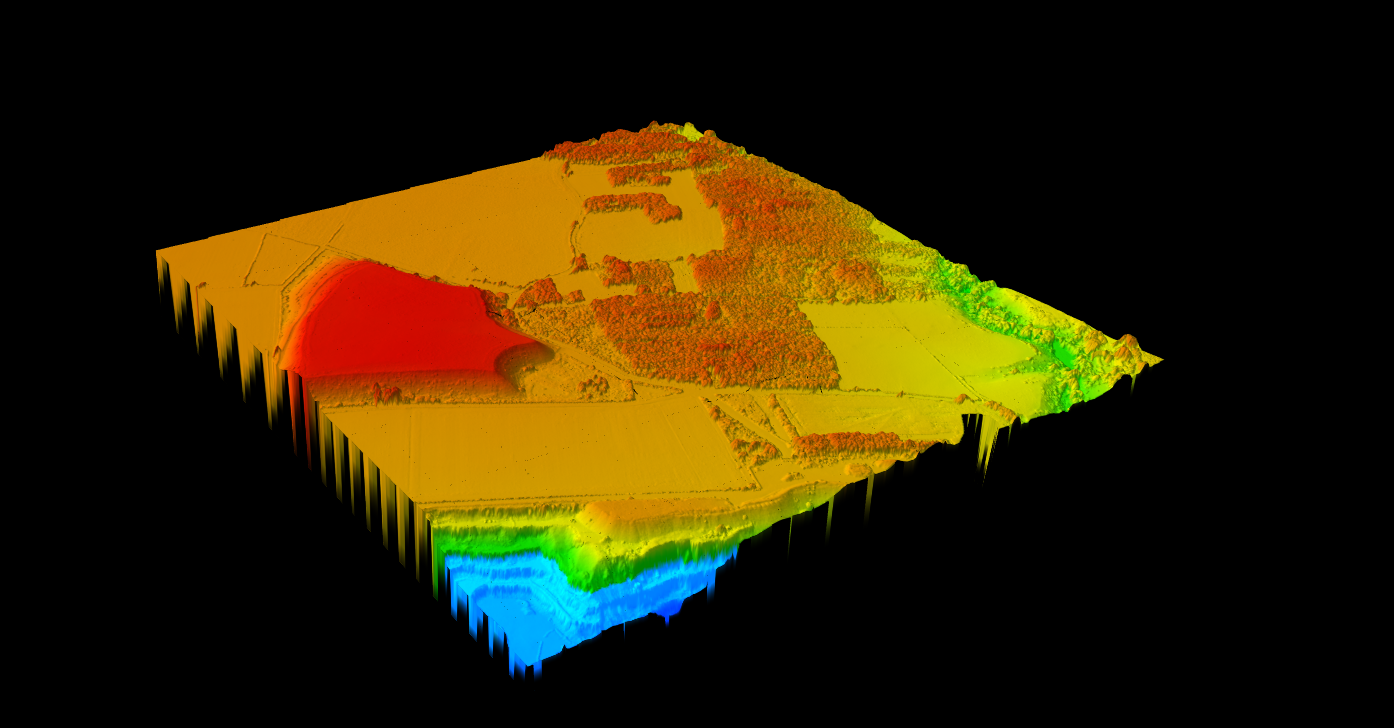
Other Creation Methods
Photogrammetry uses overlapping aerial photographs for 3D reconstruction. Lower cost but cannot penetrate vegetation and requires good lighting.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) works through clouds and at night with consistent global coverage, but offers lower resolution and requires complex processing.
LiDAR remains the gold standard for accuracy, achieving centimeter-level vertical precision with the ability to see through vegetation to the ground below.
DSM Creation Methods: LiDAR vs Photogrammetry vs Radar
While LiDAR produces the most accurate DSMs, photogrammetry and radar are viable alternatives depending on project requirements. Understanding each method’s strengths helps you choose the right approach.
| Factor | LiDAR | Photogrammetry | SAR (Radar) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface detail | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
| Building edge definition | Sharp | Moderate | Blurred |
| Vertical accuracy | 3–15 cm | 5–30 cm | 2–10 m |
| Weather dependency | Moderate | High | Low |
| Acquisition cost | High | Low–Medium | Very High (satellite) |
| Also produces imagery | No (separate) | Yes (orthomosaic) | Radar imagery |
| Best DSM applications | Urban, telecom, solar | Construction, agriculture | Regional mapping |
Choosing the Right Method for DSM
LiDAR excels for DSM creation when:
- Sharp building edges and rooflines are important (urban modeling, solar analysis)
- You also need a DTM from the same dataset (vegetation penetration is a bonus)
- The highest possible accuracy is required
- Dense vegetation or complex urban environments need to be mapped
Photogrammetry is suitable for DSM when:
- Orthoimagery is required alongside the DSM
- Cost constraints prevent LiDAR acquisition
- Surface texture and color information matter
- Weather conditions allow for clear aerial photography
Radar/SAR works for DSM when:
- Mapping large regions at moderate resolution
- Cloud cover prevents optical methods
- Free satellite data (SRTM, Copernicus DEM) meets accuracy requirements
- Change detection over time is the primary goal
For detailed method comparisons, see our LiDAR vs Photogrammetry guide.
DSM Applications
Industry Use Cases in Detail
Each industry applies Digital Surface Models differently based on their specific needs. Here’s how various sectors leverage DSM data for operational decisions.
Urban Planning and Development
Urban planners use DSMs to understand the three-dimensional form of cities. Building heights, vegetation coverage, and infrastructure are all visible in a DSM, enabling analysis that would require extensive ground surveys to replicate.
Key applications include:
- Building height enforcement: Automatically measuring building heights to verify compliance with zoning regulations
- Shadow analysis: Modeling how new construction will cast shadows on neighboring properties throughout the day and year
- Urban density assessment: Calculating built-up area ratios and floor area coverage from elevation data
- 3D city modeling: Creating textured 3D city models by draping imagery over DSM surfaces
- View corridor protection: Ensuring new development does not block protected views or sightlines
Combined with building footprint extraction, DSMs enable comprehensive urban morphology analysis.
Telecommunications and Network Planning
Telecommunications engineers rely on DSMs for radio frequency (RF) planning. Because DSMs include buildings and vegetation that block or reflect signals, they provide realistic inputs for coverage prediction models.
Common telecom applications include:
- Line-of-sight analysis: Determining whether direct signal paths exist between transmitters and receivers
- 5G small cell placement: Identifying optimal locations for millimeter-wave antennas that require direct visibility
- Clutter classification: Categorizing terrain into urban, suburban, forest, and open classes for propagation modeling
- Tower height optimization: Calculating minimum tower heights needed to achieve coverage targets
- Interference analysis: Modeling how buildings and terrain affect signal reflection and multipath
High-resolution DSMs from LiDAR are particularly valuable for dense urban environments where building geometry significantly affects signal propagation.
Forestry and Vegetation Analysis
Foresters use DSMs in combination with DTMs to measure vegetation height and structure. By subtracting the bare-earth DTM from the DSM, they create a Canopy Height Model (CHM) that reveals tree heights across the landscape.
Forestry DSM applications include:
- Canopy height mapping: Measuring tree heights at landscape scale without ground-based sampling
- Biomass estimation: Correlating canopy height and density with timber volume or carbon stock
- Forest structure analysis: Identifying gaps, edges, and layered canopy structure from elevation variation
- Fire risk modeling: Assessing fuel load and canopy connectivity that influences fire spread
- Harvest planning: Prioritizing stands for harvest based on tree height and volume estimates
Learn more about tree measurement in our tree height measurement guide and CHM explainer.
Solar Energy Assessment
Solar energy planners use DSMs to analyze rooftop and ground-mount potential. Because DSMs capture roof slopes, orientations, and surrounding obstructions, they enable accurate solar irradiance modeling.
Solar DSM applications include:
- Roof slope and aspect mapping: Classifying roof facets by orientation and tilt angle for panel placement
- Shading analysis: Modeling shadows cast by nearby buildings, trees, and terrain features throughout the year
- Usable area calculation: Identifying roof sections large enough and properly oriented for solar installations
- Energy yield estimation: Combining DSM-derived geometry with solar irradiance data to predict annual output
See our guide on LiDAR for solar farm assessment for ground-mount applications.
Aviation and Drone Operations
Aviation safety depends on accurate knowledge of obstacles that penetrate controlled airspace. DSMs provide the comprehensive obstacle data needed for approach path analysis and drone corridor planning.
Aviation applications include:
- Obstacle identification: Detecting buildings, towers, and vegetation that may affect flight operations
- Approach path analysis: Verifying clearance along instrument approach and departure paths
- Drone corridor planning: Designing safe flight paths for beyond-visual-line-of-sight (BVLOS) operations
- Terrain awareness: Providing elevation data for ground proximity warning systems
- Airspace management: Supporting low-altitude airspace authorization for urban air mobility
Resolution and Accuracy
| Data Source | Resolution | Vertical Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite (SRTM, ASTER) | 30m | 2–5m RMSE |
| Aerial Photogrammetry | 5–10m | 0.5–2m RMSE |
| Aircraft LiDAR | 1–2m | 5–15cm RMSE |
| Drone LiDAR | 0.1–0.5m | 3–10cm RMSE |
Creating DSMs with Lidarvisor
No software to install. No parameters to tune. Lidarvisor simplifies DSM generation from LiDAR point clouds in four steps:
- Upload your LAS or LAZ point cloud file
- Automatic classification labels points as ground, vegetation, buildings, and more
- DSM generation creates the first-return surface model automatically
- Download as GeoTIFF ready for GIS analysis
The same process generates both DSM and DTM products, along with hillshade visualization for easy interpretation.
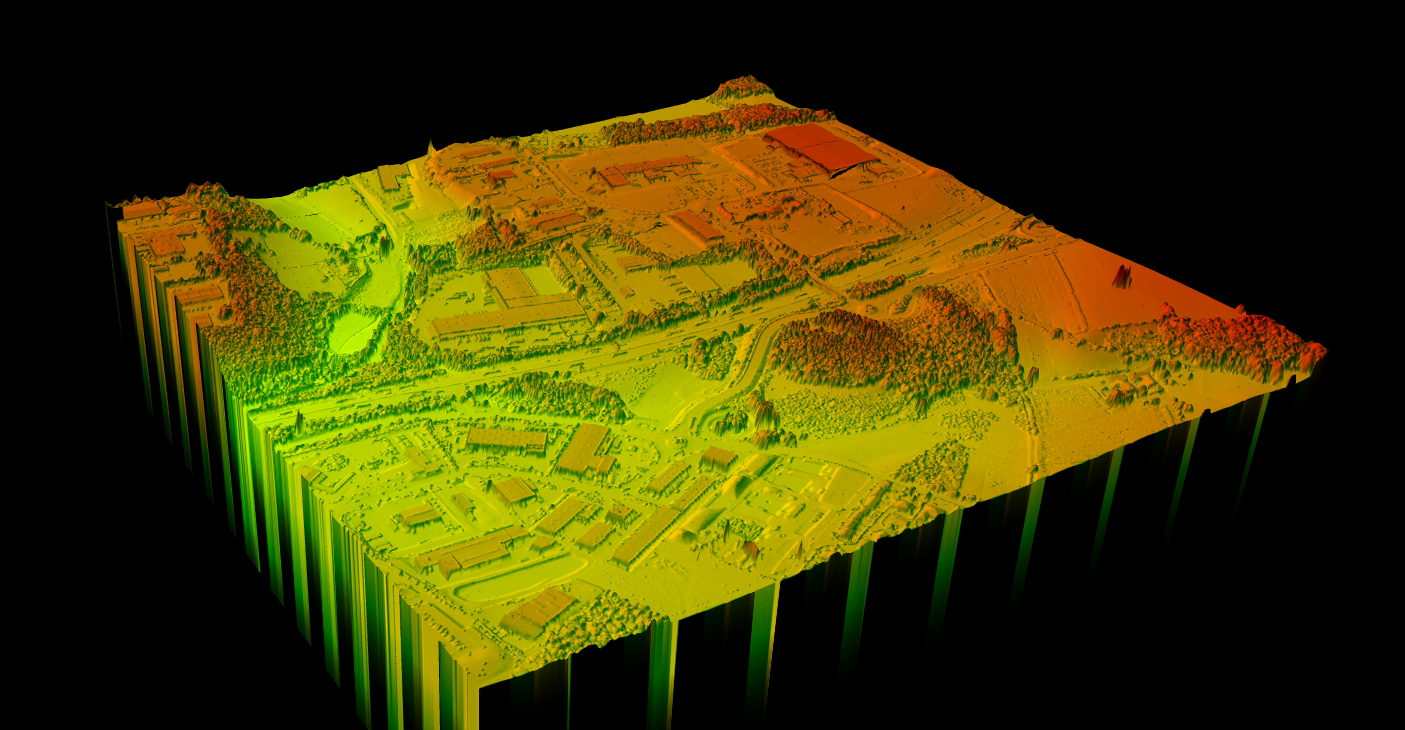
Frequently Asked Questions
A DSM includes all visible surfaces like buildings and trees, while a DTM shows only the bare ground with all objects removed. Use DSM when surface features matter (urban planning, telecom); use DTM for terrain analysis (hydrology, engineering).
Accuracy depends on the acquisition method. LiDAR-derived DSMs achieve 5–15 cm vertical accuracy. Photogrammetric DSMs from aerial imagery typically reach 0.5–2 m accuracy. Satellite-derived DSMs have 2–5 m accuracy or more.
Yes. Drone photogrammetry or drone LiDAR both produce high-quality DSMs. Photogrammetry requires 70–80% image overlap and processing through structure-from-motion software. Drone LiDAR provides higher accuracy and works under vegetation.
DSMs are typically stored as GeoTIFF files, georeferenced raster images where each pixel contains an elevation value. Other formats include ASCII grid, ESRI Grid, and various proprietary formats. Lidarvisor exports DSMs as standard GeoTIFF files compatible with all major GIS software.
Ask what you need to analyze:
- Need to see buildings and trees? Use DSM
- Need bare ground for drainage/grading? Use DTM
- Need object heights? Use both, then calculate nDSM
Resolution requirements vary by application:
- Urban planning: 1–2 meter resolution captures building outlines and major vegetation
- Telecom RF planning: 1–5 meter resolution, depending on frequency band and environment
- Solar rooftop analysis: 0.25–0.5 meter resolution to capture roof detail and obstructions
- Forestry CHM: 1–2 meter resolution for canopy height, 0.5 meter for individual tree detection
- Construction monitoring: 0.1–0.25 meter for detailed progress tracking
Higher resolution requires denser point cloud data and increases file sizes significantly. Match resolution to your actual analysis needs.
A Canopy Height Model (CHM) measures vegetation height above ground. Create it by subtracting the DTM from the DSM:
CHM = DSM − DTM
This works because the DSM records the top of the vegetation canopy, the DTM records the bare ground surface beneath, and the difference equals the height of vegetation above ground.
In GIS software, this is a simple raster subtraction operation. The result shows tree heights in meters, with zero values in open areas. Learn more in our CHM guide.
Yes, several free global DSMs are available:
- Copernicus DEM GLO-30: 30-meter resolution global coverage, available through the Copernicus programme
- SRTM: 30-meter resolution for most of the world (60°N to 56°S)
- ASTER GDEM: 30-meter global coverage, though with more noise than SRTM
- ALOS World 3D: 30-meter global DSM from Japanese satellite data
These are suitable for regional analysis but lack the resolution and accuracy of LiDAR-derived DSMs. Building edges are blurred, and vertical accuracy is typically 2–5 meters rather than centimeters.
Several visualization techniques help interpret DSM data:
- Hillshade: Simulated lighting reveals terrain and building form through shadows
- Color gradient: Apply color ramps to show elevation variation (low=blue, high=red)
- 3D perspective: Drape orthoimagery or color over the DSM for realistic 3D views
- Contour lines: Generate isolines showing elevation intervals
- Slope map: Calculate surface gradient to highlight steep areas
Lidarvisor automatically generates hillshade visualization alongside DSM output for immediate interpretation.
Common DSM artifacts include:
- Data voids: Areas with no elevation data, often caused by water surfaces that absorb laser pulses or shadowed areas
- Edge effects: Blurred or jagged building edges from insufficient point density or interpolation method
- Moving objects: Vehicles, aircraft, or birds captured during scanning may appear as artifacts
- Multipath reflections: False returns from reflective surfaces like glass or water
- Scan line artifacts: Visible stripe patterns from sensor or flight path irregularities
Quality classification and filtering reduce artifacts. Lidarvisor’s automatic processing handles common issues like removing vehicles and noise points.
