Understanding LiDAR Point Cloud Files
Related Articles
What Is a LAS File?
A LAS file (LASer file format) is an open, binary format designed for the interchange and archiving of LiDAR point cloud data. Developed and maintained by the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ASPRS), the LAS format has been the industry standard since 2003.
Each LAS file contains thousands to billions of 3D points, where each point includes X, Y, Z coordinates, intensity (return signal strength), classification code, return number, GPS time (optional), and RGB color values (optional).
LAS files are stored as binary data with a defined header structure, making them efficient to read and write compared to text-based formats.
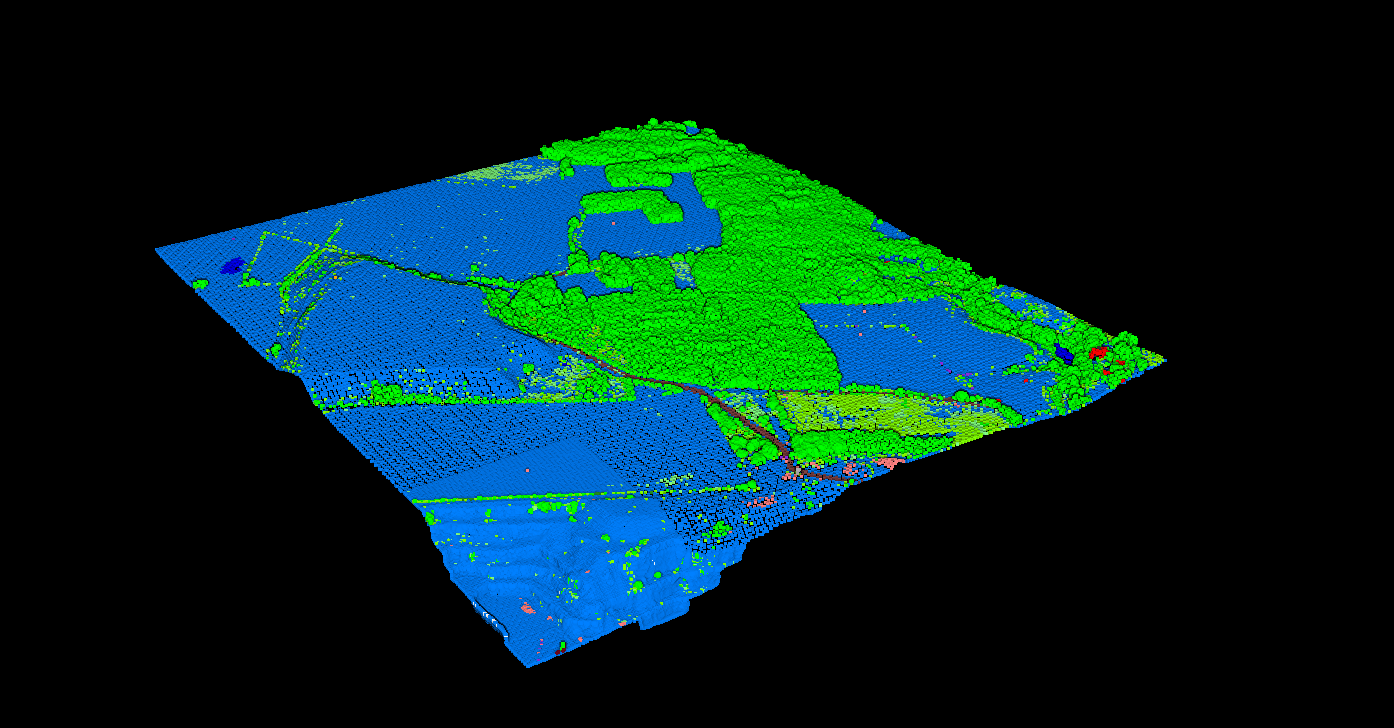
LAS File Structure
Every LAS file follows a defined structure with four main sections that organize metadata and point data efficiently.
| Section | Description | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Public Header Block | File metadata | Version, point count, bounding box, scale factors, CRS |
| Variable Length Records | Extended metadata | Projection info, custom data (max 65,535 bytes each) |
| Point Data Records | Point cloud data | X, Y, Z, intensity, classification, returns, time, color |
| Extended VLRs | Large metadata (LAS 1.3+) | Waveform data, large payloads after point data |
LAS Versions: 1.2 vs 1.3 vs 1.4
The LAS specification has evolved to support new sensor capabilities. The current version is LAS 1.4 R15 (July 2019).
| Version | Release | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| LAS 1.2 | 2008 | Core format with classification, intensity, GPS time. Point formats 0-3. Most compatible. |
| LAS 1.3 | 2010 | Waveform support (formats 4-5), EVLRs for larger metadata payloads. |
| LAS 1.4 | 2011 | 64-bit point count, 256 classification codes, NIR channel. Point formats 6-10. |
Point Data Record Formats
The Point Data Record Format (PDRF) determines what attributes are stored for each point. Format 3 is most common for aerial LiDAR.

What Is a LAZ File?
LAZ is the lossless compression of LAS files developed by Martin Isenburg (rapidlasso). LAZ files are structurally identical to LAS but compressed, reducing file sizes to 7-25% of the original.
When to use LAZ: Storage, archiving, file transfer, cloud hosting. LAZ is now a de facto industry standard.
When to use LAS: Legacy software compatibility or when maximum read performance is critical.
The compression is completely lossless—every point and attribute is preserved exactly.
LAS vs LAZ Comparison
| Aspect | LAS | LAZ |
|---|---|---|
| Compression | None | Lossless (7-25% of LAS) |
| Data Loss | None | None |
| Read Speed | Faster | Slightly slower |
| File Size | Larger | Much smaller |
| Compatibility | Universal | Widely supported |
LAS Classification Codes
The ASPRS standard defines classification codes for common features. LAS 1.4 expanded support to 256 codes. Learn more in our LiDAR classification guide.
| Code | Classification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Ground | Bare earth surface points |
| 3-5 | Vegetation | Low, medium, and high vegetation |
| 6 | Building | Building rooftops and structures |
| 7 | Low Point | Noise points below surface |
| 9 | Water | Water bodies |
| 14-15 | Wire/Tower | Power lines and transmission towers |
How to Process LAS Files
Raw LAS files from a LiDAR sensor typically need processing before they are useful. Lidarvisor automates this workflow.
01
Upload
Upload your LAS or LAZ point cloud file to the cloud platform.
02
Classification
AI-powered classification labels ground, vegetation, buildings automatically.
03
Product Generation
DTM, DSM, contours, and hillshade generated from classified points.
04
Download
Export classified LAS, GeoTIFF rasters, and vector products.
How to Open LAS Files
Free Online Viewer
Our free LAS file viewer works directly in your browser. No installation required.
Desktop Software
- CloudCompare: Free, open-source point cloud viewer
- QGIS: Free GIS with native LAS support (3.18+)
- Global Mapper: Commercial GIS with excellent LAS handling
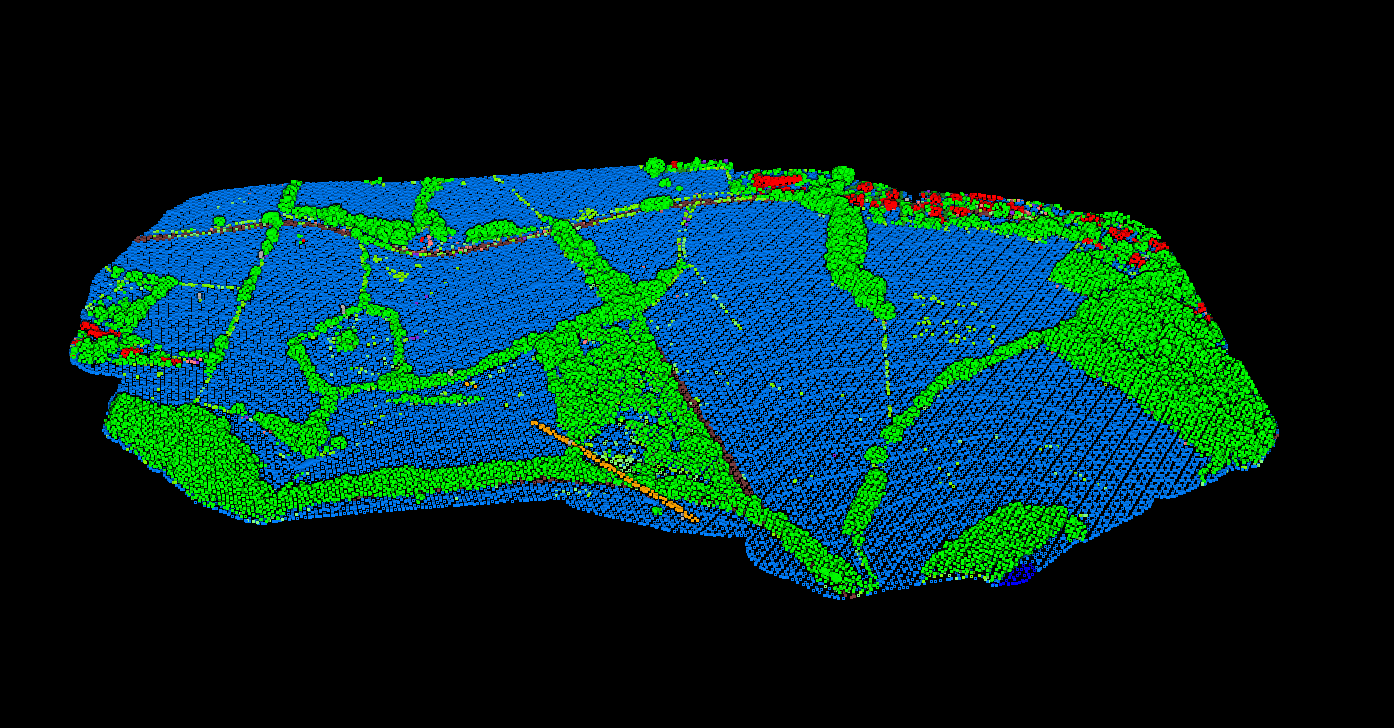
LAS Applications
Frequently Asked Questions
LAS is the uncompressed format while LAZ is the lossless compressed version. LAZ files are 7-25% the size of LAS files with no data loss. Most modern software supports both formats.
For maximum compatibility with older software, use LAS 1.2. For modern drone LiDAR and high-density scans requiring more than 32 classification codes, use LAS 1.4. Most processing software can convert between versions.
Use our free online LAS viewer at lidarvisor.com/las-file-viewer for quick visualization. For desktop work, CloudCompare (free) or QGIS (free) both support LAS and LAZ files natively.
Some LAS files lack coordinate reference system (CRS) information in their Variable Length Records. Check the header for GeoTIFF tags or WKT definitions. If missing, you may need to manually assign the correct CRS in your GIS software.
COPC (Cloud Optimized Point Cloud) extends LAZ for cloud-native workflows. COPC files organize point data into an octree structure, enabling efficient streaming without downloading the entire file. It is the point cloud equivalent of Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF.
Create a FREE account now and start processing your point cloud
Get 2 GB of storage space and classify up to 10 hectares for free.
