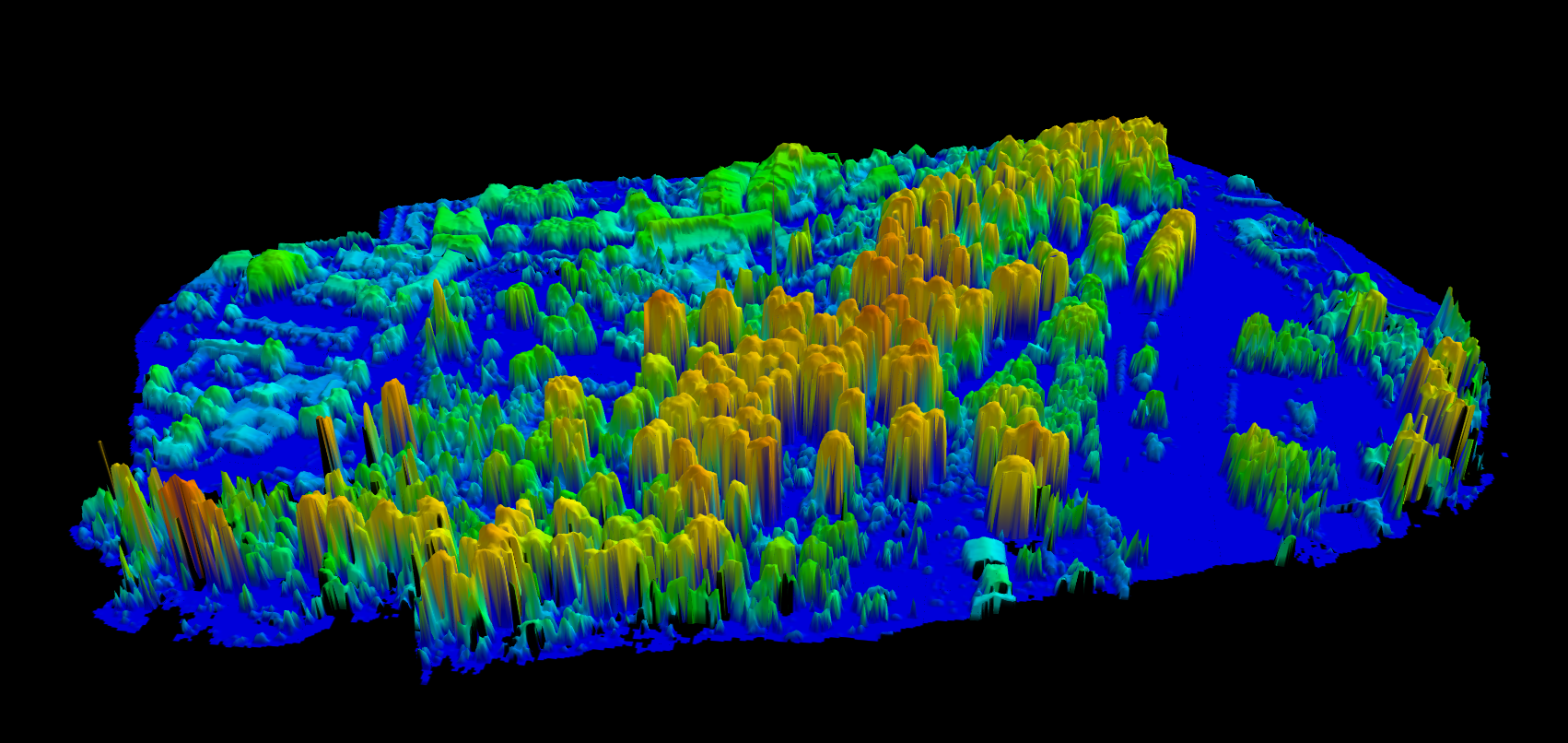
A Canopy Height Model shows vegetation height above the ground — not elevation above sea level, but the actual height of trees measured from their base to their crown. For forestry, ecology, and carbon accounting, the CHM is often the most valuable product derived from LiDAR data.
The Simple Calculation
CHM = DSM – DTM
Take the Digital Surface Model (capturing the top of the canopy) and subtract the Digital Terrain Model (capturing the ground below). What remains is the vegetation height at every point.
If a tree’s crown sits at 145 meters elevation and the ground beneath it sits at 120 meters, that tree stands 25 meters tall.
This calculation works across the entire survey area, producing a raster where every cell contains a height value. Tall trees appear as high values; shrubs appear as low values; bare ground appears as zero.
What CHMs Enable
The quality of a CHM depends directly on the quality of its inputs. Errors in ground classification propagate into terrain model errors, which cascade into height errors. Getting the DTM right is essential.
Generate Accurate CHMs with LidarVisor
LidarVisor generates accurate CHMs by first producing high-quality terrain models through AI-powered ground classification. Use them for tree detection, height statistics, or export for analysis in your forestry software.
