Habitat Mapping & Impact Assessment
Why Environmental Consultants Use LiDAR
Traditional field surveys provide ground-truth data but are limited in coverage and repeatability. LiDAR complements fieldwork by providing:
Habitat Mapping & Vegetation Analysis
LiDAR excels at characterizing vegetation structure across large areas. Environmental consultants use classified point clouds to:
- Map vegetation height classes (low, medium, high vegetation)
- Identify tree crowns and canopy gaps for forest structure analysis
- Calculate canopy height models (CHM) by subtracting DTM from DSM
- Detect hedgerows and fencelines that serve as wildlife corridors
- Quantify understory vegetation using multi-return penetration
This structural information feeds directly into habitat suitability models for species of concern.
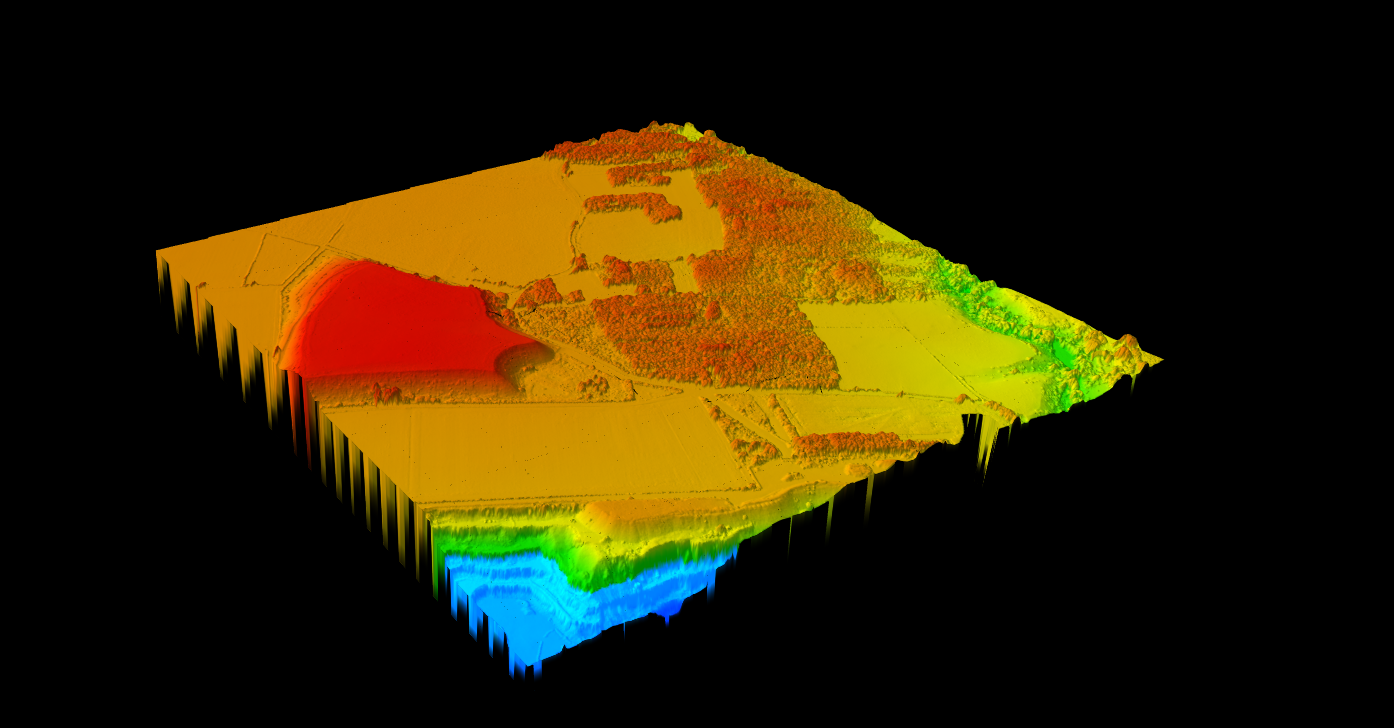
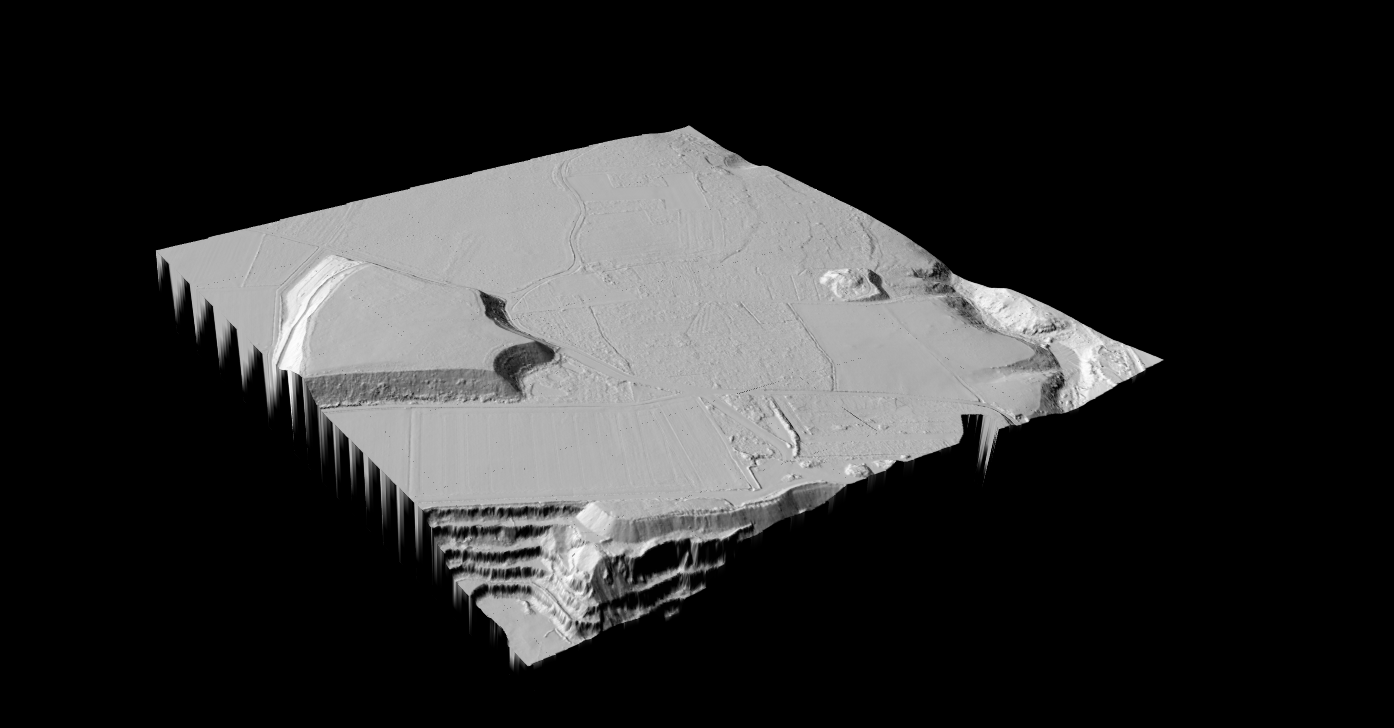
Wetland Delineation & Water Features
Accurate wetland boundaries require precise topographic data. LiDAR provides:
- Water body segmentation from classified point clouds
- High-resolution DTMs for identifying subtle topographic breaks
- Slope analysis for drainage pattern identification
- Microtopography mapping critical for hydric soil predictions
Combined with field verification, LiDAR-derived boundaries are defensible in regulatory reviews and jurisdictional determinations.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
Impact assessments require comprehensive baseline documentation. LiDAR supports EIA by providing:
Pre-Construction Baseline
Terrain models for comparison and change monitoring.
Vegetation Inventory
Complete data across the project footprint for impact quantification.
Sensitive Area Mapping
Steep slopes, drainage ways, riparian zones identified automatically.
Visual Impact Analysis
3D surface models for stakeholder presentations and planning.
Disturbance Calculations
Quantified area and volume metrics for mitigation planning.
Erosion & Sediment Analysis
Erosion risk assessment relies on accurate terrain characterization:
- Slope maps identify areas prone to erosion
- DTMs enable flow accumulation modeling
- Repeat surveys quantify erosion and deposition volumes
- Channel morphology analysis for stream restoration
Riparian & Corridor Analysis
Linear features like streams and wildlife corridors require special attention:
- Buffer zone vegetation characterization
- Stream bank height and stability assessment
- Floodplain mapping for regulatory compliance
- Connectivity analysis for habitat fragmentation studies
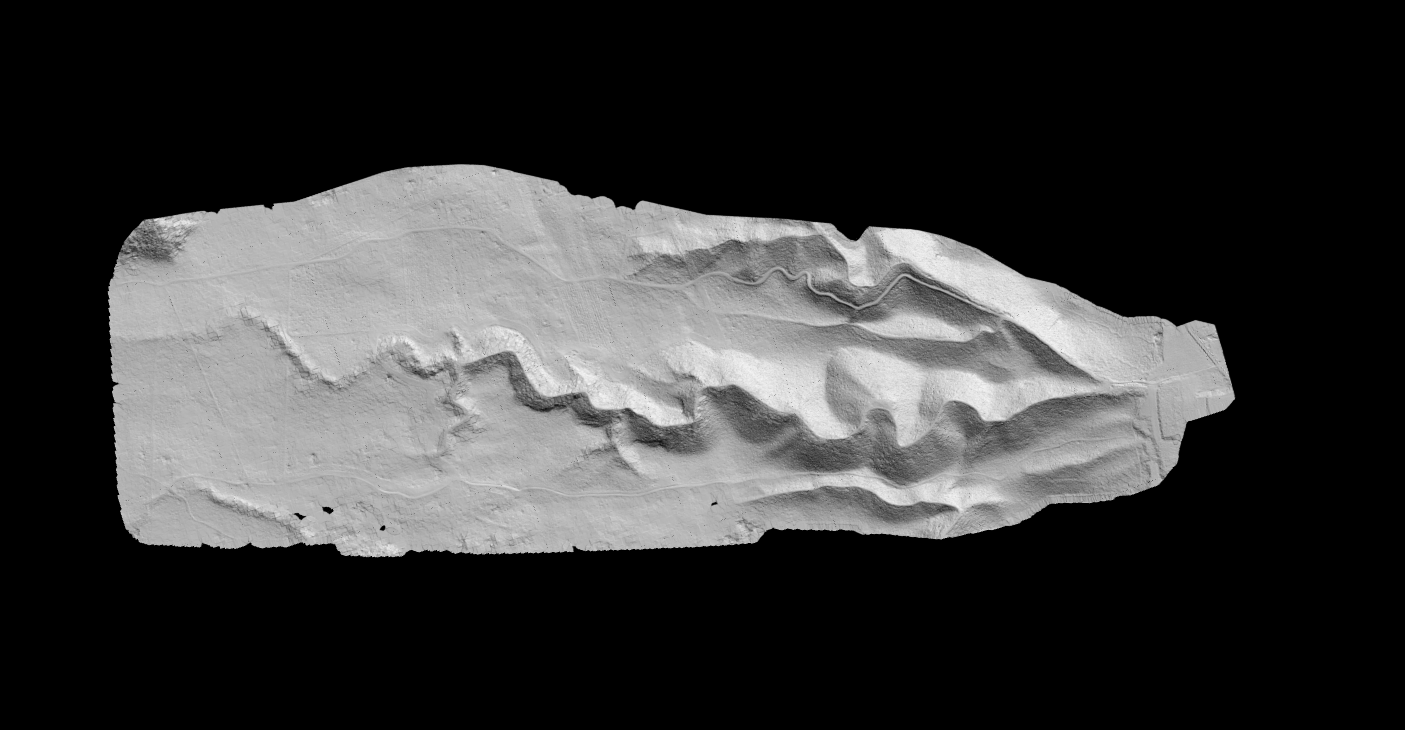
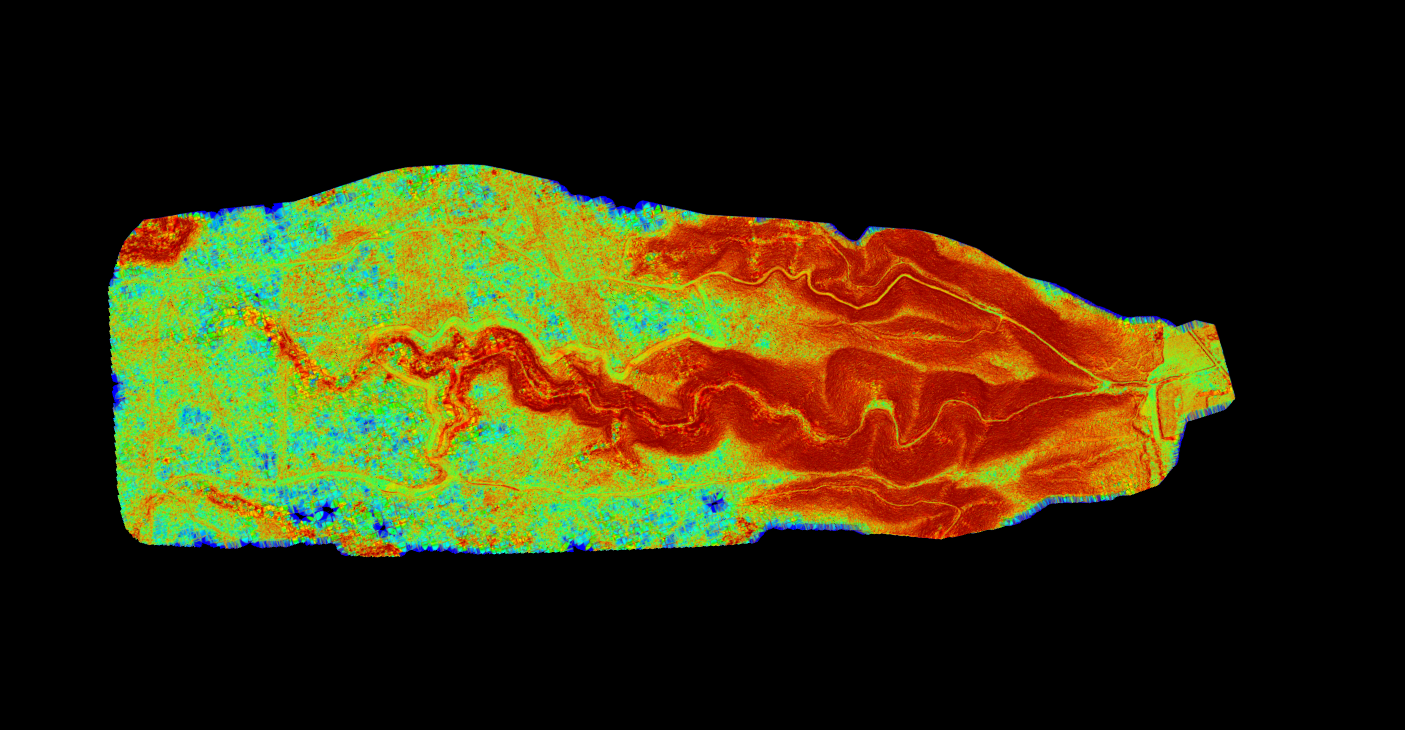

LiDAR Products for Environmental Work
Environmental projects typically require several derived products from the classified point cloud:
DTM (Digital Terrain Model)
Wetland boundaries, drainage analysis, erosion modeling
DSM (Digital Surface Model)
Canopy coverage, visual impact, total vegetation height
Canopy Height Model
Habitat structure, forest inventory, species modeling
Slope Map
Erosion risk, habitat gradients, drainage direction
Hillshade
Terrain visualization, report graphics, field navigation
Classified Point Cloud
Custom analysis, 3D visualization, data archive
Contour Lines
Traditional mapping, CAD integration, construction docs
Tree Crowns/Tops
Individual tree inventory, species counts, canopy gaps
Processing LiDAR for Environmental Projects
Environmental consultants often acquire LiDAR data from drone surveys, public repositories, or contracted flights. Regardless of source, the raw point cloud requires processing before it becomes useful.
Traditional Approach
Desktop software with manual parameter tuning for classification, separate tools for raster generation, and extensive QC review. This workflow requires specialized training and significant time investment.
Streamlined with Lidarvisor
Upload your point cloud and receive classified data plus derived products (DTM, DSM, slope, contours, vegetation layers) without parameter adjustment. Minutes, not days.
What Lidarvisor Classifies
Lidarvisor’s AI-powered classification identifies 12 feature classes relevant to environmental work:
Additional classes (wire, pole, tower, vehicle, bridge deck, roof objects) support infrastructure-related environmental assessments. All outputs include the classified point cloud for QC review in your preferred GIS software.
Workflow Example: Habitat Assessment
01
Data Acquisition
Drone survey or download from public sources (USGS 3DEP, state repositories)
02
Point Cloud Classification
Upload to Lidarvisor for automatic processing
03
Product Generation
Export DTM, vegetation layers, and canopy height model
04
GIS Analysis
Import products into ArcGIS or QGIS for habitat modeling
05
Field Verification
Ground-truth key findings with site visits
06
Reporting
Generate maps and statistics for deliverables
Lidarvisor compresses steps 2-3 from hours or days into minutes, letting consultants focus on analysis and interpretation rather than data wrangling.
Data Sources for Environmental Projects
Environmental consultants access LiDAR data from multiple sources:
- Custom drone surveys — Highest resolution, project-specific timing
- USGS 3DEP — Free coverage across much of the United States
- State and county GIS portals — Often higher resolution than federal data
- NOAA Digital Coast — Coastal areas and bathymetric data
- International repositories — UK Environment Agency, European national surveys
Combining sources allows cost-effective coverage: use public data for regional context and commission custom flights for critical project areas.
Ready to Streamline Your Environmental LiDAR Workflow?
Start with a test project. Upload a point cloud from a recent site to see how automated classification and product generation can accelerate your work. Process up to 10 hectares at no cost.
