How Classified Point Clouds Power Smarter Energy Planning
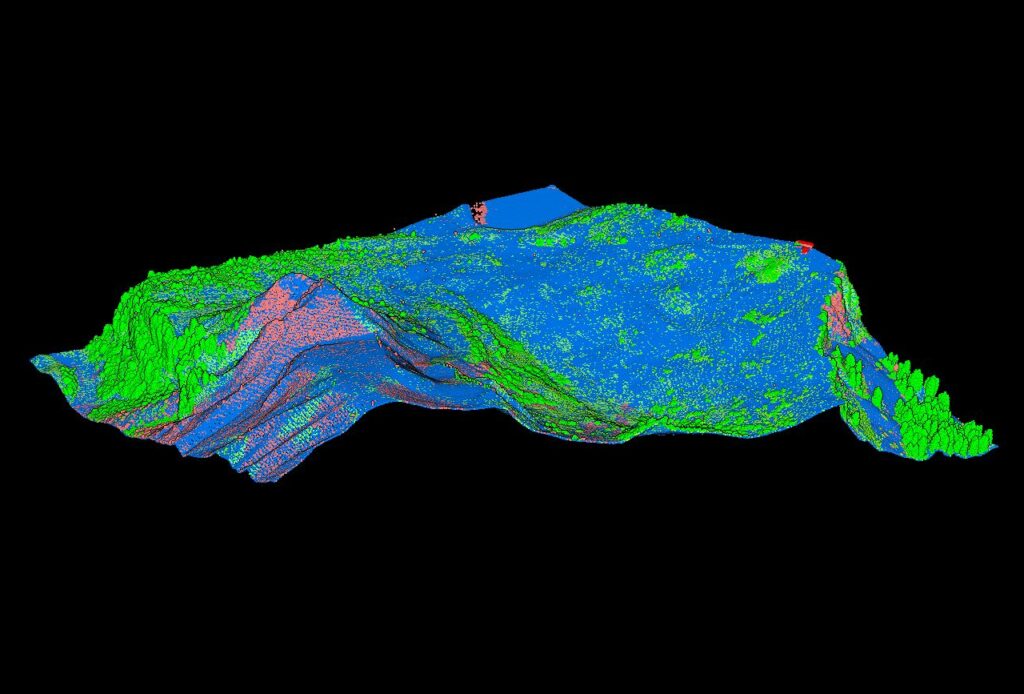
How Airborne LiDAR Works
By emitting thousands of laser pulses per second, LiDAR measures reflection times to determine distances. Each reflected point creates a three-dimensional map representing terrain, structures, and vegetation with centimeter-level precision.


3D Perspective for Strategic Planning
One of the primary benefits of LiDAR is its ability to provide a 3D view of terrains, even the most intricate ones. For engineers planning energy infrastructure, this equates to a gold mine of information, facilitating technical and strategic decision-making.
The comprehensive terrain data enables planners to identify optimal routes for power lines, assess terrain stability for wind turbines, and evaluate shadow patterns for solar installations.
Why Classification Matters
Imagine a puzzle with millions of pieces. That’s the challenge posed by an unclassified LiDAR point cloud. By segmenting this data into distinct categories, classification transforms this puzzle into a clear and interpretable picture.
AI-Powered Classification
Artificial intelligence and machine learning play a pivotal role in point cloud classification. These technologies help identify and distinguish minute details, from rivers to power lines, offering unprecedented precision in LiDAR data analysis.
Modern AI classifiers can automatically separate ground, vegetation, buildings, and infrastructure with remarkable accuracy, saving weeks of manual work.
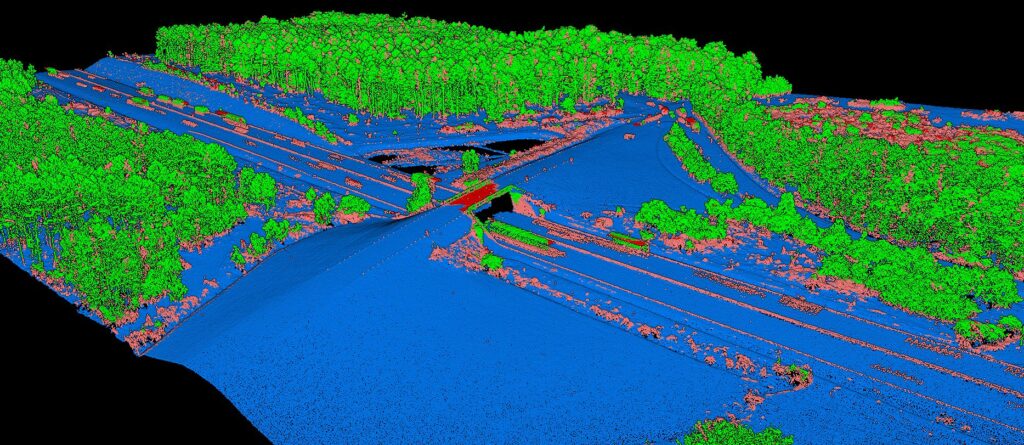
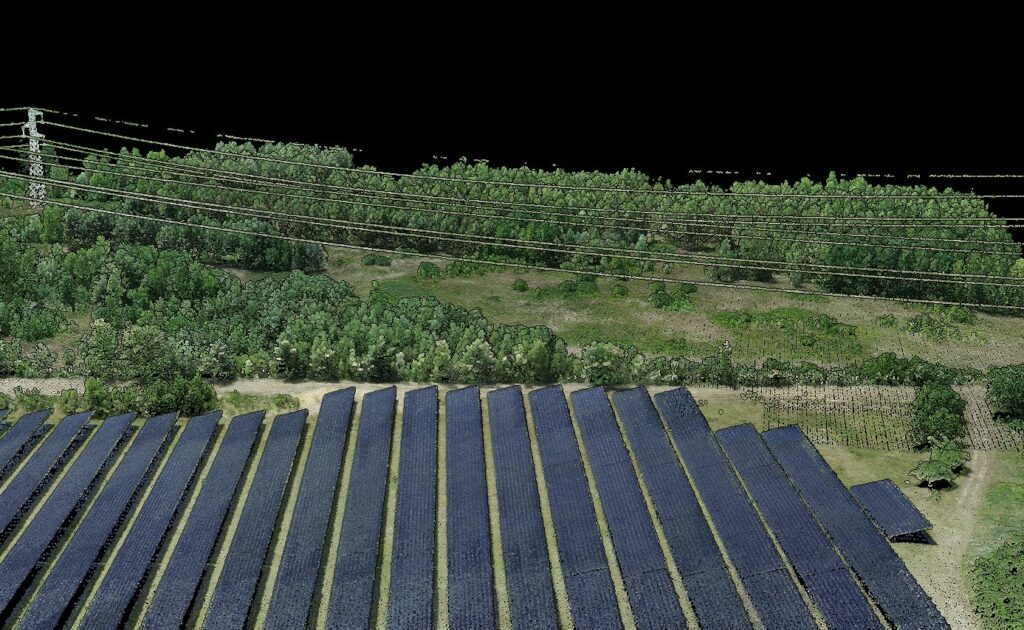
Renewable Energy Applications
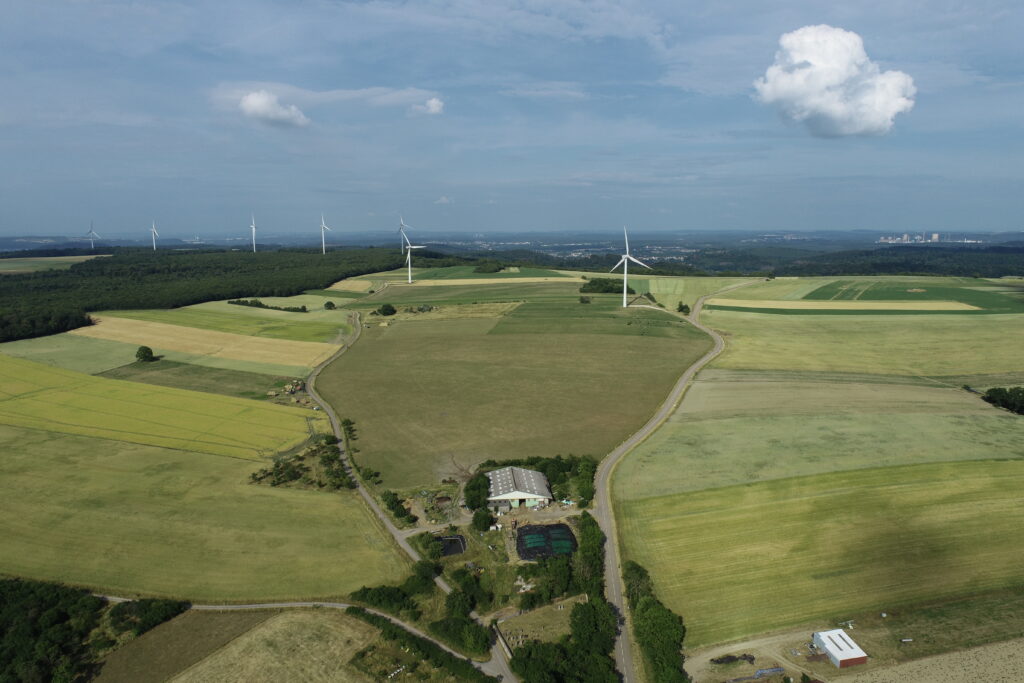

Wind Farm Planning
The wind potential of a region depends not only on wind speed but also on its consistency, orientation, and the topography of the terrain. Wind farms, often located in remote areas, require accurate terrain knowledge before installation.
In Denmark, a pioneer in wind energy, LiDAR has revolutionized terrain and air current modeling. By creating 3D maps of targeted regions, engineers can pinpoint areas with the most consistent winds and identify obstacles that might disrupt airflow, optimizing turbine placement and maximizing energy production.
Solar Power Plants
A solar power plant’s efficiency largely relies on the amount of sunlight it can capture. Precise terrain analysis is crucial to maximize this capture.
In California, LiDAR has become an invaluable tool for solar developers. By accurately mapping terrain, LiDAR identifies areas with consistent sunlight while avoiding shadows from hills or obstructions. The technology also analyzes ground reflectivity, critical for bifacial solar panels that capture light on both sides.

Fossil Energy Applications
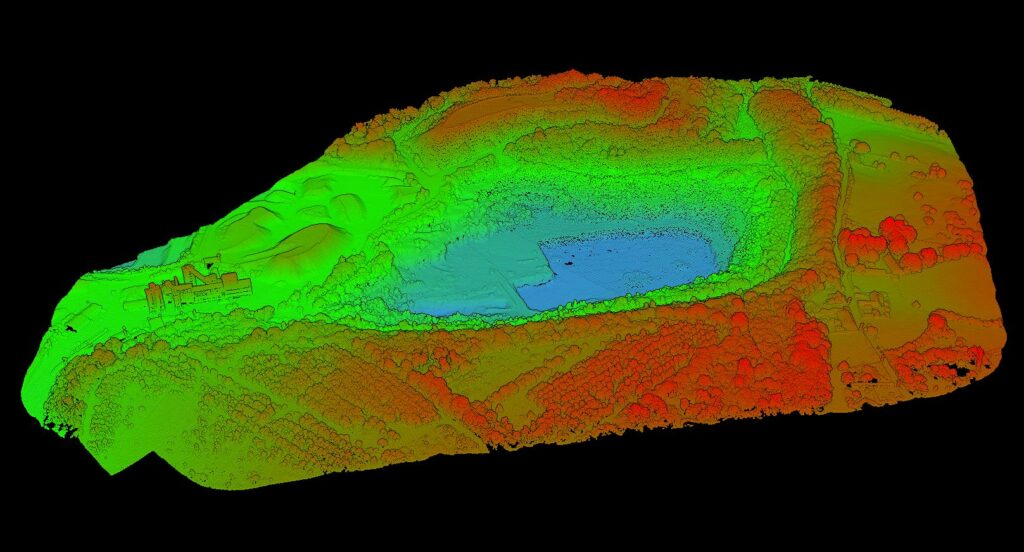
Oil and Gas Extraction
In Alberta, Canada’s oil sands region, precision cannot be overstated. LiDAR maps potential access areas, helping define the best equipment routes while minimizing environmental impact.
By precisely identifying vegetation, water bodies, and ecological features, LiDAR allows a more environmentally conscious approach, reducing impact on fauna and flora while ensuring efficient exploitation.
Pipeline Installation
In Alaska, with its wilderness and extreme conditions, LiDAR proves invaluable for pipeline planning. The technology accurately identifies risk areas including geological faults, flood zones, and protected species habitats, leading to safer construction and optimal routing.
Electrical Grid Management
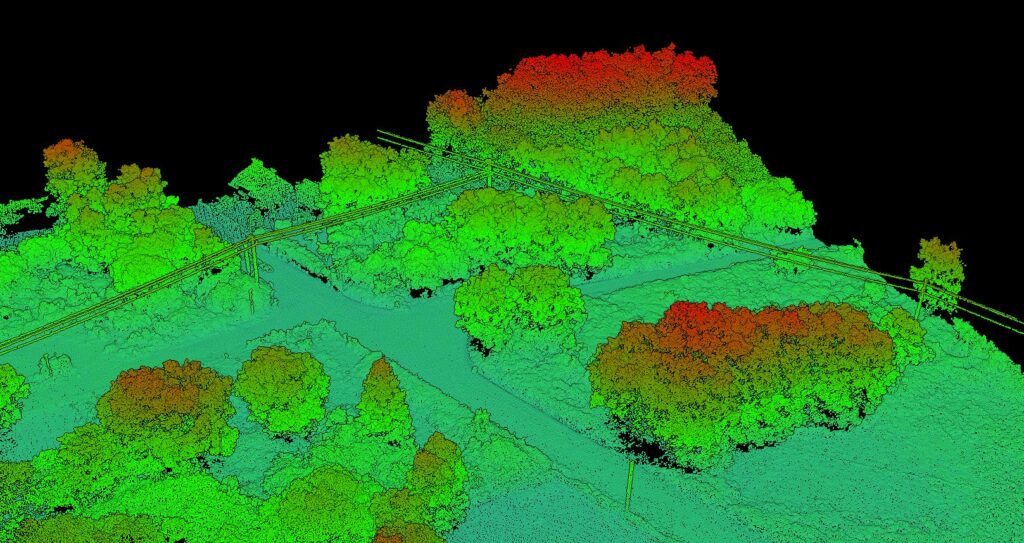
Transmission Line Planning
Establishing high-voltage transmission lines demands meticulous terrain mapping. Airborne LiDAR simplifies gathering comprehensive data on landscapes, natural barriers, and pre-existing infrastructures.
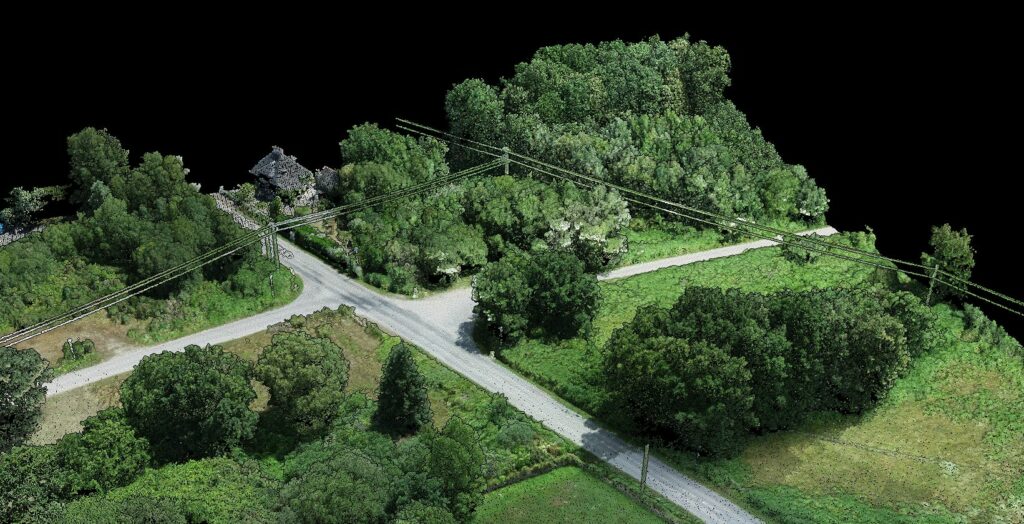

Corridor Monitoring
Preserving electrical corridor integrity is paramount. Using classified LiDAR data, grid managers can oversee corridors and spot potential hazards like unchecked vegetation growth near transmission lines.

Drone Surveillance
Drones equipped with LiDAR sensors have become instrumental in proactive maintenance, navigating corridors to detect anomalies and relay them to ground teams for swift interventions.
The Future of LiDAR in Energy
As LiDAR technologies and classification methodologies continue to evolve, we’re ushered into a transformative phase of energy infrastructure planning. The fusion of LiDAR with advanced classification, underpinned by cutting-edge artificial intelligence, equips us with a sharper, more holistic, and dependable outlook to navigate the energy challenges of the future.
